SLAE64 - Assignment 1 - TCP Bind Shell with passcode
The first assigment for the SLAE64 certification asks to write a TCP Bind Shell shellcode that listens on a port and then executes a shell after verifying a “passcode” on successful connection.
For the basic structure of a Bind Shell TCP, please refer to assignment 5 and to related assignment for the SLAE32 certification.
In order to verify the passcode, a code section has been added after the dup2 cycle, in order to perform a read syscall which puts the 8 bytes read on the stack and compares with the hardcoded passcode (acceptme).
If the comparison is successful, then the execve is performed:
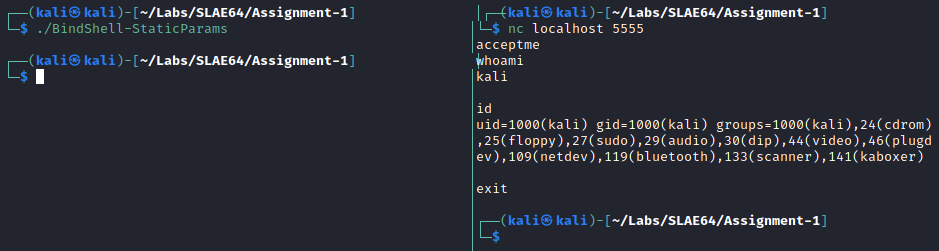
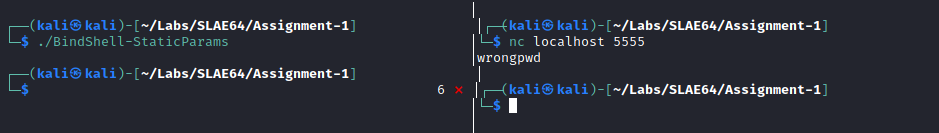
If the submitted passcode is wrong, the program exits with status code 6:
Customization Utility
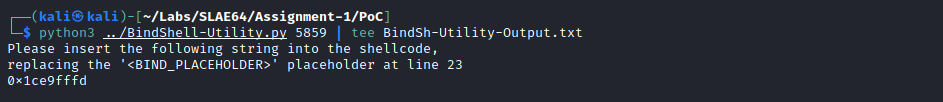
In order for the reverse shell to be customizable, the BindShell-Skeleton.nasm file has been created with a placeholders to be filled with appropriate chosen port (line 23).
Given that the bytes have to be inserted as XOR-ed with 0xFF, in order to avoid null ones, the BindShell-Utility.py comes handy as it just requires to be executed passing the IP and Port for the connection as parameters, and appropriate value will be calculated and presented to the user:
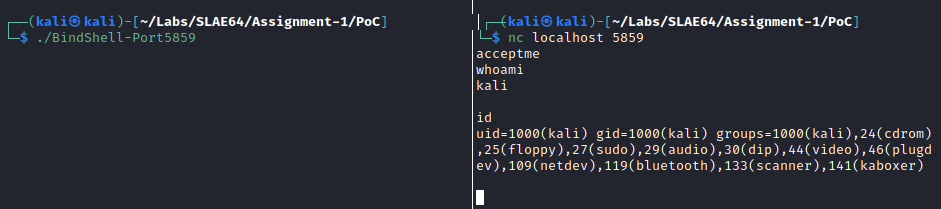
The following screenshot shows the shell listening on port 5859, for which the parameter has been generated with the Python utility:
This blog post has been created for completing the requirements of the SecurityTube Linux Assembly Expert certification: http://www.securitytube-training.com/online-courses/x8664-assembly-and-shellcoding-on-linux/index.html.
Student ID: PA-29059
GitHub repository: https://github.com/andrea-perfetti/SLAE64-Exam
This assignment has been written on a Kali Linux 2021.1 64-bit virtual machine:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ uname -a
Linux kali 5.10.0-kali3-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.13-1kali1 (2021-02-08) x86_64 GNU/Linux
